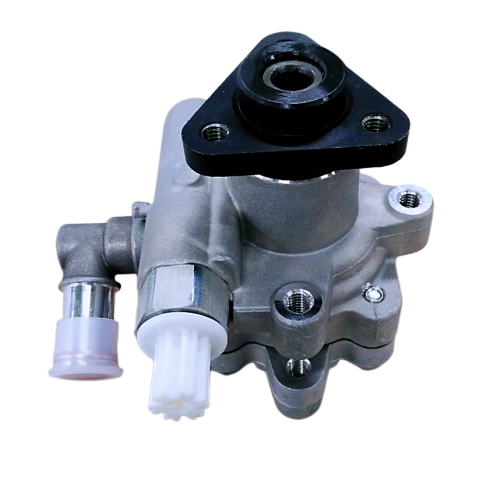
제품 세부 사항

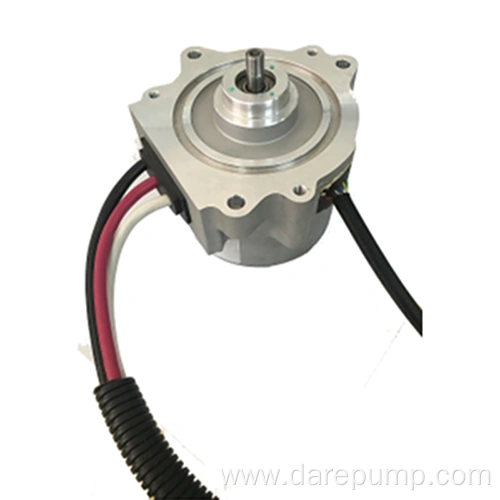
자동 변속기 보조 오일 펌프
- 설명
-
Product Attributes
Model No.:FBB127C
Brand:FZB
Place Of Origin:China
Application:DCT
Type:Vane PumpPackaging & Delivery
Selling Units:Piece/Pieces
Package Type:PAPER BOX, PALLETProduct Description
The function of the oil pump of the transmission is to provide hydraulic pressure to operate the control valve and clutch, provide a quantitative supply of gear oil in the transmission and differential boxes, and send the transmission oil to the cooler for circulation and heat dissipation. The following is a partial introduction to the oil pump:
The oil pump is the power source of the entire hydraulic system of the automatic transmission, and is generally directly driven by the engine.
All automatic transmissions have a front pump driven by an engine, and some transmissions also have a rear pump driven by an output shaft. The commonly used oil pumps include internal gear oil pumps, rotor type oil pumps, and vane type oil pumps.
There are two oil pumps in the gearbox, which are installed in an assembly and separated by a partition between them. They operate at the same speed and rotate at the same speed as the engine.
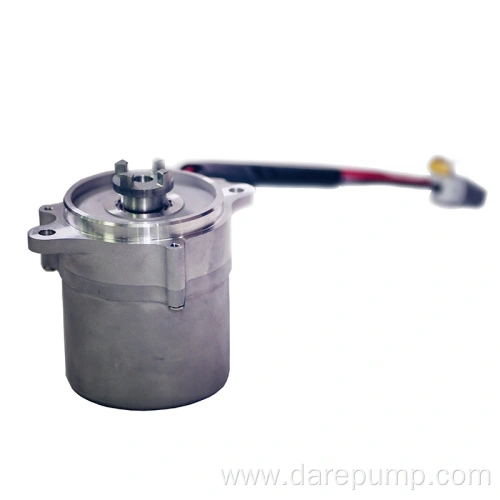
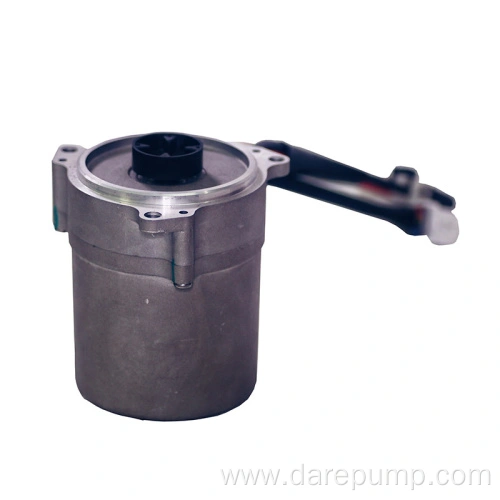
Critical parametersPart Name Transmission Oil Pump Function Master Oil Pump DARE PN FBB127C Application DCT Type of Pump Vane Pump Max. Pressure 25bar Speed Range 650-6600rpm Flow Rate >=7.4L/min Working Temperature -40 to 140℃ Vane pump
This vane pump has the advantages of stable operation, low noise, uniform oil flow, and high volumetric efficiency. However, its structure is complex and sensitive to hydraulic oil contamination. As shown in the figure, the pump consists of a stator, rotor, blade, housing, and pump cover. The rotor is driven by a shaft sleeve at the rear of the torque converter housing and rotates around its center. The stator is fixed, and the two are not concentric, with a certain degree of eccentricity. When the rotor rotates, the blades open outward under the action of centrifugal force and oil pressure at the bottom of the blades, close to the inner surface of the stator, and reciprocate in the rotor blade groove as the rotor rotates. Therefore, a sealed working chamber is formed between adjacent blades. If the rotor rotates clockwise, the volume of the working chamber in the right half of the connecting line between the rotor and the stator gradually increases, resulting in vacuum oil absorption. The volume of the working chamber in the left half of the center line gradually decreases, and the oil pressure is extracted. Operating principle: The rotor is driven by the shaft sleeve of the hydraulic torque converter housing, rotates around its center, and the stator is fixed. The rotor and stator are not concentric, and there is eccentricity between them. When the rotor rotates, under the action of centrifugal force, the blades expand outward, close to the inner surface of the stator, and reciprocate in the rotor blade groove as the rotor rotates, thereby forming a sealed working cavity between adjacent blades. If the rotor rotates clockwise, the volume of the working chamber on the right side of the center line of the rotor and stator will gradually increase, creating a certain degree of vacuum. The hydraulic oil will be sucked in from the oil inlet, and the volume of the working chamber on the left side of the center line of the rotor and stator will gradually decrease. The hydraulic oil pressure will increase, and the oil will be discharged from the oil outlet.
제품 컨설팅
* 참고: 정보를 정확하게 기입하고 통신을 차단하지 마십시오. 가능한 한 빨리 연락 드리겠습니다.